Balanced Diet and Macronutrients
Discover the essentials of a balanced diet and the role of macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in maintaining optimal health. Learn how to create a diet that fuels your body and supports long-term well-being.

Image Credit/https://health.osu.edu/
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to a Balanced Diet
- What is a Balanced Diet?
- Why is a Balanced Diet Important?
- Understanding Macronutrients
- Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Energy Source
- Proteins: The Building Blocks of Life
- Fats: Essential for Health and Vital Functions
- The Role of Each Macronutrient in a Balanced Diet
- The Importance of Carbohydrates
- Protein Needs for Different Individuals
- Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats: Making the Right Choice
- How to Calculate Your Macronutrient Needs
- Determining Your Daily Caloric Needs
- Macronutrient Ratios: What’s Right for You?
- Tools and Apps for Tracking Macronutrients
- Practical Tips for Incorporating Macronutrients into Your Diet
- Meal Planning for a Balanced Diet
- Healthy Food Choices for Each Macronutrient
- Portion Control and Balanced Meal Examples
- Common Myths About Macronutrients
- Myth: Carbs Are Bad for You
- Myth: You Need High Protein for Muscle Gain
- Myth: All Fats Lead to Weight Gain
- FAQs on Balanced Diet and Macronutrients
- What happens if I don’t get enough macronutrients?
- Can I lose weight by just adjusting my macronutrient intake?
- How do macronutrient needs change with age?
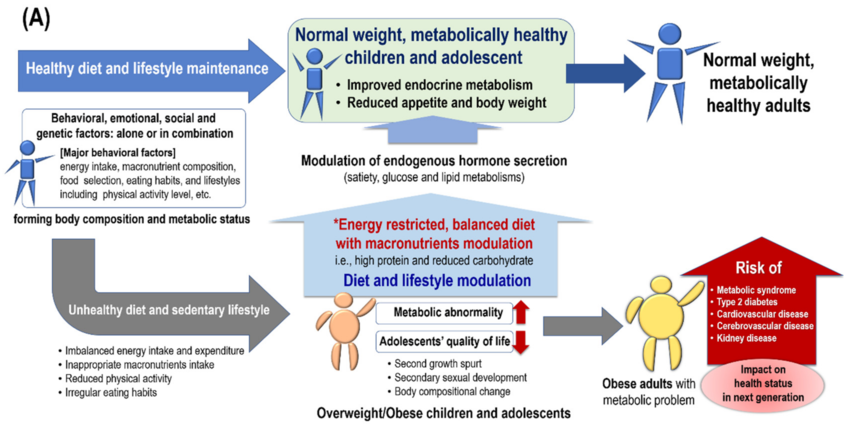
Image Credit/https://www.researchgate.net/
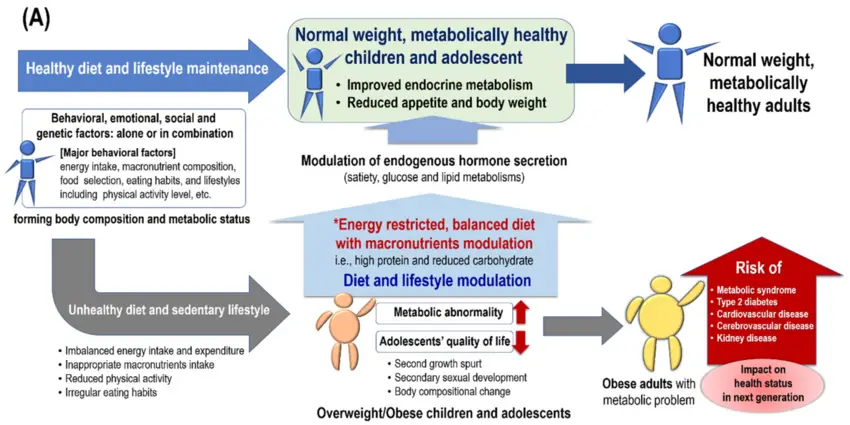
Introduction to a Balanced Diet
What is a Balanced Diet?
A balanced diet is a nutritional approach that includes the right proportions of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—along with essential vitamins and minerals. It’s the foundation of good health, providing the energy and nutrients your body needs to function optimally.
Why is a Balanced Diet Important?
Eating a balanced diet ensures that your body gets the nutrients it needs to maintain energy levels, support growth and repair, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It’s not just about counting calories; it’s about nourishing your body with a variety of foods that contribute to your overall well-being.
Understanding Macronutrients
Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for your body, especially for your brain and muscles. They come in two main types: simple and complex. Simple carbs provide quick energy, while complex carbs offer sustained energy and are found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
Proteins: The Building Blocks of Life
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, making enzymes, hormones, and other body chemicals. They are also crucial for muscle mass and immune function. Sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, dairy, beans, and nuts.
Fats: Essential for Health and Vital Functions
Fats are not just a source of energy; they are vital for brain health, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. There are different types of fats—saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats—each with different effects on health. The key is to focus on healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.

Image Credit/https://quizlet.com/
The Role of Each Macronutrient in a Balanced Diet
The Importance of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates should make up about 45-65% of your daily caloric intake. They fuel your body and provide the energy needed for physical activity and proper organ function.
Protein Needs for Different Individuals
Protein intake varies depending on age, sex, and activity level. Generally, protein should account for 10-35% of your daily calories. Athletes and those involved in heavy physical work may need more protein to support muscle repair and growth.
Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats: Making the Right Choice
Not all fats are created equal. Unsaturated fats, found in foods like fish, nuts, and olive oil, are beneficial, while trans fats and excessive saturated fats can increase the risk of heart disease. Aim for fats to make up about 20-35% of your daily intake.
How to Calculate Your Macronutrient Needs
Determining Your Daily Caloric Needs
Your daily caloric needs depend on factors like age, gender, weight, height, and physical activity level. Once you know your caloric needs, you can divide them into the appropriate macronutrient ratios.
Macronutrient Ratios: What’s Right for You?
Common macronutrient ratios include 40% carbs, 30% protein, and 30% fat. However, these ratios can be adjusted based on personal goals, such as weight loss, muscle gain, or specific dietary preferences.
Tools and Apps for Tracking Macronutrients
There are several tools and apps available to help you track your macronutrient intake, such as MyFitnessPal, Cronometer, and Lose It! These apps can simplify the process and help you stay on track with your dietary goals.
Practical Tips for Incorporating Macronutrients into Your Diet
Meal Planning for a Balanced Diet
Planning your meals ahead of time ensures that you get a good balance of macronutrients throughout the day. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods and aim for variety.
Healthy Food Choices for Each Macronutrient
- Carbohydrates: Whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes.
- Proteins: Lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, tofu, and legumes.
- Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish.
Portion Control and Balanced Meal Examples
Portion control is key to maintaining a balanced diet. For example, a balanced meal might include grilled chicken (protein), quinoa (carbohydrates), and a mixed green salad with olive oil dressing (fats).
Common Myths About Macronutrients
Myth: Carbs Are Bad for You
Carbohydrates have been unfairly demonized in recent years. The truth is, they are essential for energy, especially for brain function. The key is choosing complex carbs over simple sugars.
Myth: You Need High Protein for Muscle Gain
While protein is important for muscle repair, consuming excessively high amounts of protein doesn’t necessarily lead to more muscle gain. Balance is crucial, and other nutrients also play a role.
Myth: All Fats Lead to Weight Gain
Not all fats are equal. Healthy fats are necessary for bodily functions and can actually aid in weight loss by promoting satiety and reducing overall calorie intake.
FAQs on Balanced Diet and Macronutrients
Q1: What happens if I don’t get enough macronutrients?
A lack of macronutrients can lead to energy deficiencies, muscle loss, hormonal imbalances, and other health issues. It’s important to consume a balanced mix to support overall health.
Q2: Can I lose weight by just adjusting my macronutrient intake?
Yes, adjusting your macronutrient ratios can help with weight loss, but it should be combined with overall calorie control and regular physical activity for the best results.
Q3: How do macronutrient needs change with age?
As you age, your body’s metabolism slows down, and you may require fewer calories. However, protein needs may increase to prevent muscle loss, and the focus should be on nutrient-dense foods.
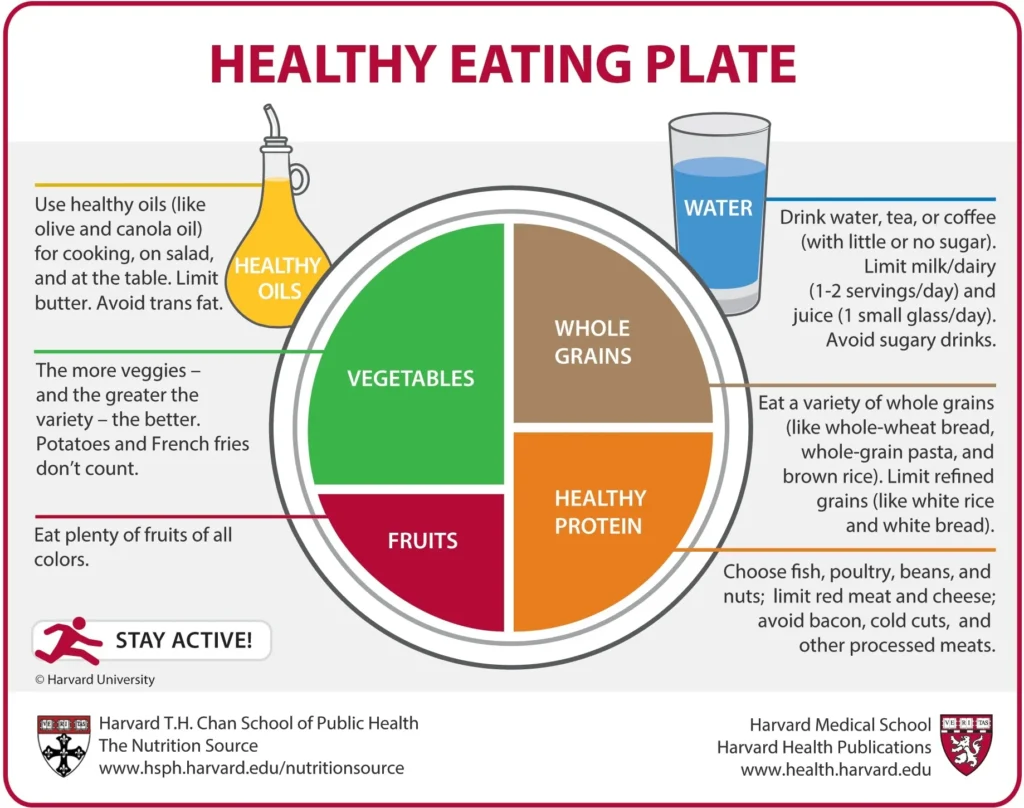
Image Credit/https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/
Conclusion
A balanced diet rich in the right proportions of macronutrients is crucial for maintaining energy levels, supporting bodily functions, and promoting long-term health. By understanding and incorporating the right mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into your diet, you can ensure that your body gets the nourishment it needs to thrive.