Understanding Heart Disease
Explore the essentials of heart disease, including its types, risk factors, symptoms, and prevention strategies. Learn how to recognize and manage heart disease for a healthier life.
Image Credit/https://clinic.cardiovisual.com/
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Heart Disease
- What is Heart Disease?
- The Prevalence of Heart Disease
- Types of Heart Disease
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Heart Failure
- Arrhythmias
- Valvular Heart Disease
- Risk Factors for Heart Disease
- Modifiable Risk Factors
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Symptoms of Heart Disease
- Common Symptoms
- Symptoms in Women vs. Men
- Diagnosis and Testing
- Common Diagnostic Tests
- How Heart Disease is Diagnosed
- Treatment and Management
- Lifestyle Changes
- Medications
- Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures
- Preventing Heart Disease
- Healthy Eating Habits
- Exercise and Physical Activity
- Managing Stress and Other Factors
- FAQs About Heart Disease
- What are the early signs of heart disease?
- How can I reduce my risk of heart disease?
- Is heart disease hereditary?
Image Credit/https://ssbhealthcare.com/
Introduction to Heart Disease
What is Heart Disease?
Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that affect the heart’s structure and function. It encompasses various disorders of the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and valvular heart disease. These conditions can impact the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, leading to complications and potentially serious health issues.
The Prevalence of Heart Disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it accounts for a significant percentage of deaths globally, emphasizing the need for awareness, prevention, and effective management.
Image Credit/https://cvrti.utah.edu/
Types of Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease is caused by the buildup of plaque (a combination of fat, cholesterol, and other substances) in the coronary arteries. This buildup narrows the arteries and reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, which can lead to chest pain (angina) or heart attacks.
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently to meet the body’s needs. This can result from various conditions, including CAD, high blood pressure, or heart valve issues. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention.
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats caused by disruptions in the heart’s electrical system. Common types include atrial fibrillation (AFib), ventricular tachycardia, and bradycardia. These irregularities can lead to complications such as stroke or heart failure.
Valvular Heart Disease
Valvular heart disease involves damage to or dysfunction of one or more of the heart’s valves. This can disrupt normal blood flow within the heart. Conditions include valve stenosis (narrowing of the valve) and valve regurgitation (leaking of the valve).
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Modifiable Risk Factors
- High Blood Pressure: Increases the heart’s workload, leading to damage to the arteries.
- High Cholesterol: Contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and increases the risk of CAD.
- Diabetes: Can lead to high blood sugar levels that damage blood vessels.
- Obesity: Associated with higher risks of high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise contributes to various risk factors for heart disease.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk at a younger age, but women’s risk increases after menopause.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase your risk.
- Genetics: Genetic predispositions can affect the likelihood of developing heart disease.
Symptoms of Heart Disease
Common Symptoms
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: Often described as pressure, squeezing, or fullness.
- Shortness of Breath: Can occur with or without chest pain.
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness or weakness.
- Palpitations: Irregular or rapid heartbeats.
Symptoms in Women vs. Men
Women may experience symptoms differently from men. While chest pain is a common symptom for both genders, women are more likely to experience other symptoms such as nausea, shortness of breath, and extreme fatigue. It’s important for women to be aware of these atypical signs.
Diagnosis and Testing
Common Diagnostic Tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical activity of the heart to identify arrhythmias and heart damage.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to create images of the heart’s structure and function.
- Stress Test: Assesses how the heart performs under physical stress.
- Blood Tests: Detects markers of heart damage, such as troponins.
How Heart Disease is Diagnosed
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Your healthcare provider will assess symptoms, risk factors, and results from tests to diagnose heart disease and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment and Management
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or DASH diet, to reduce cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity to strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on the heart.
Medications
- Statins: Lower cholesterol levels.
- Antihypertensives: Control blood pressure.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: Reduce the risk of blood clots.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures
- Angioplasty and Stenting: Procedures to open narrowed arteries and improve blood flow.
- Bypass Surgery: Creates a new route around blocked arteries.
- Heart Valve Surgery: Repairs or replaces damaged heart valves.
Preventing Heart Disease
Healthy Eating Habits
- Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and high-cholesterol foods.
Exercise and Physical Activity
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Incorporate strength training and flexibility exercises.
Managing Stress and Other Factors
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
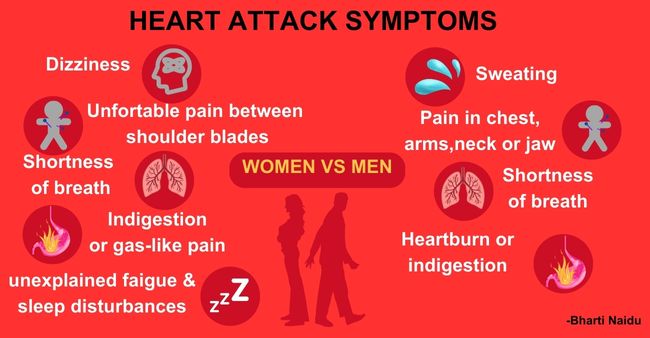
Image Credit/https://thedailyguardian.com/
FAQs About Heart Disease
Q1: What are the early signs of heart disease?
Early signs of heart disease can include chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and irregular heartbeats. However, symptoms can vary, and some people may not experience noticeable symptoms until a more serious issue arises.
Q2: How can I reduce my risk of heart disease?
Reducing your risk involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle: eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, manage stress, avoid smoking, and control conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes.
Q3: Is heart disease hereditary?
Yes, genetics can play a role in heart disease. A family history of heart disease can increase your risk, but lifestyle factors and health management also significantly impact your risk level.
Conclusion
Understanding heart disease is crucial for effective prevention and management. By recognizing the types, risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to protect your heart health and enhance your overall well-being. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness are key to staying heart-healthy.